Describe the Structural Organization of a Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome
DNA is organized into multiple linear chromosomes found in the nucleusDue to haploid genomeprokaryotes can grow and incr. Coli Continues bidirectionally Chromosome attached to plasma membrane.
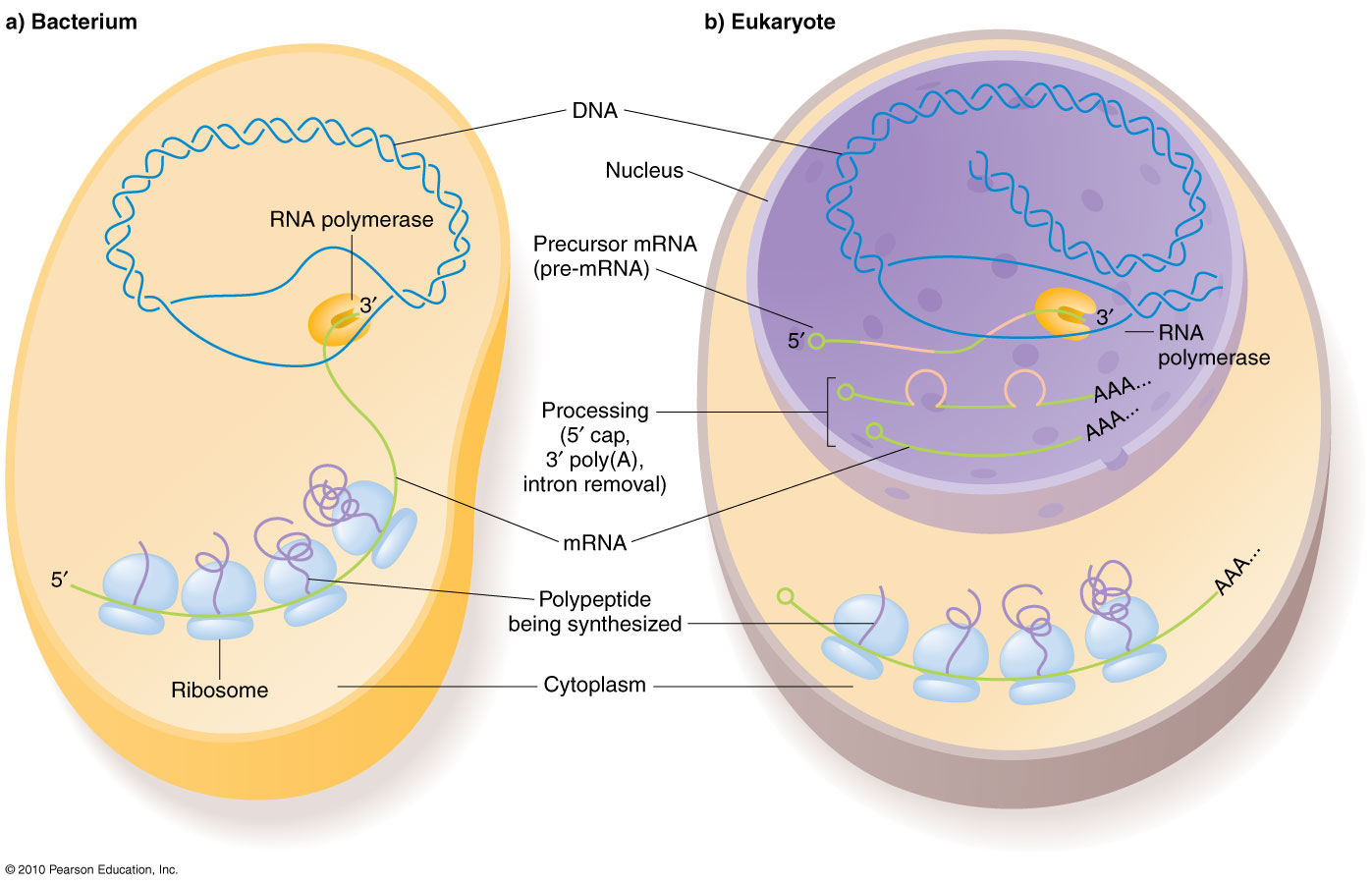
Transcription In Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes
Describe the major events of cell division that enable the genome of one cell to be passed on to two daughter cells.
. Describe the content of the human and mammalian. Escherichia coli is taken as model organism for the study of prokaryotic chromosomes because they are simple easily available easily grown in culture broth and less pathogenic. Where are the prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA found.
As in eukaryotic cells DNA supercoiling is necessary for the genome to fit within the prokaryotic cell. A genophore is the DNA of a prokaryote. It is commonly referred to as a prokaryotic chromosome.
Describe the major events of cell division that enable the genome of one cell to be passed on to two daughter cells. The genome of a eukaryotic cell consists of the chromosome housed in the nucleus and extrachromosomal DNA found in the mitochondria all cells and chloroplasts plants and algae. Eukaryotic Gene Structure Although humans contain a thousand times more DNA than do bacteria the best estimates are that humans have only about 20 times more genes than do the bacteria.
Eukaryotic are packed into chromosomes in a double helix shape. Up to 24 cash back organization and control of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome. Main Difference Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic DNA.
These vital interactions depend on the chromosome structure as a molecule and on the genome organization as a unit of genetic information. As with eukaryotes topoisomerases are involved in supercoiling DNA. Eukaryotes consist of membrane-bound nucleus whereas prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus.
Strong selection for the organization of the genetic e. Contrast the size and organization of prokaryotic versus eukaryotic genomes. Circular DNA Condensed by packaging proteins eg.
The genetic material can be seen as a fairly compact clump or series of clumps that occupies about a third of the volume of the cell named NUCLEOID. The genome of prokaryotic organisms generally is a circular double-stranded piece of DNA multiple copies of which may exist at any time. The prokaryotic DNA is found in a coiled loop floating in the cytoplasm whereas the eukaryotic DNA is found inside the nucleus.
Prokaryotic genomes are found in a single strand of DNA in a circular shape. Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of chromatin a complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division In animals somatic cells have two sets of chromosomes and gametes have one set of chromosomes human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes and gametes have 23 chromosomes 10. In addition to organization of DNA in prokaryotes and lower eukaryotes in eukaryotes the DNA helix is highly organised into the well-defined DNA-protein complex termed as nucleosomes.
The length of a genome varies widely but is generally at least a few million base pairs. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA carry genetic information for the development functioning and reproduction of prokaryotes and eukaryotes respectively. Among the proteins the most prominent are the histones.
Coli consists of a single closed-circular DNA molecule of 46 million base pairs length. Prokaryotic genome organization Each bacterial chromosome is made by a single circular DNA molecule rarely linear. Eukaryotic are packed into chromosomes in a double helix shape.
Prokaryotic genomes are exemplified by the E. A cells DNA packaged as a double-stranded DNA molecule is called its genome. Prokaryotic DNA is double-stranded and circular.
This means that the vast majority of eukaryotic DNA is apparently nonfunctional. The histones are small and basic proteins rich in amino acids such as lysine andor arginine. DNA gyrase is a type of topoisomerase found in bacteria and some archaea that helps prevent the overwinding of.
Replication starts at ori oriCin E. Prokaryotes because they have simple structural organization compared to eukaryotes. Prokaryotic genomes are found in a single strand of DNA in a circular shape.
Compare the structure and organisation of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes in terms of size packing of DNA linearitycircularity presence of introns and type of regulatory sequences. Besides chromosomes some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that may contain one or a few genes not essential for normal growth see Figure 1 in Unique. Usually each cell contain one single copy of each chromosome.
In prokaryotes the genome is composed of a single double-stranded DNA molecule in the form of a loop or circle Figure 1. In most viruses and prokaryotes the single set of genes is stored in a single chromosome single molecule either RNA or DNA. The DNA in E.
1Prokaryotes are typically haploid usually having a single circular chromosome found in the nucleoid. Describe the structure and function of the portions of eukaryotic DNA that do not. Define genome as the complete set of genes or genetic material present in a cell or organism.
The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid remember that prokaryotes do not have a separate membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotes are monoploid they have only one set of genes one copy of the genome. The DNA in the bacterial chromosome is arranged in several supercoiled domains.
The cytoplasm of prokaryotes contains many molecular machines interacting directly with the chromosome. Explain why genome size does not predict organismal complexity or phylogeny and vice versa. Prokaryotic DNA is a closed circular structure whereas eukaryotic DNA is linear.

Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Dna Replication Comparison Summary 1 Dna Replication Dna Molecular Genetics

Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Genome Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Gene Structure Pediaa Com

Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Differences Examples

Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Differences Structure Capsule
What Is The Structure Of Prokaryotic Cells Quora
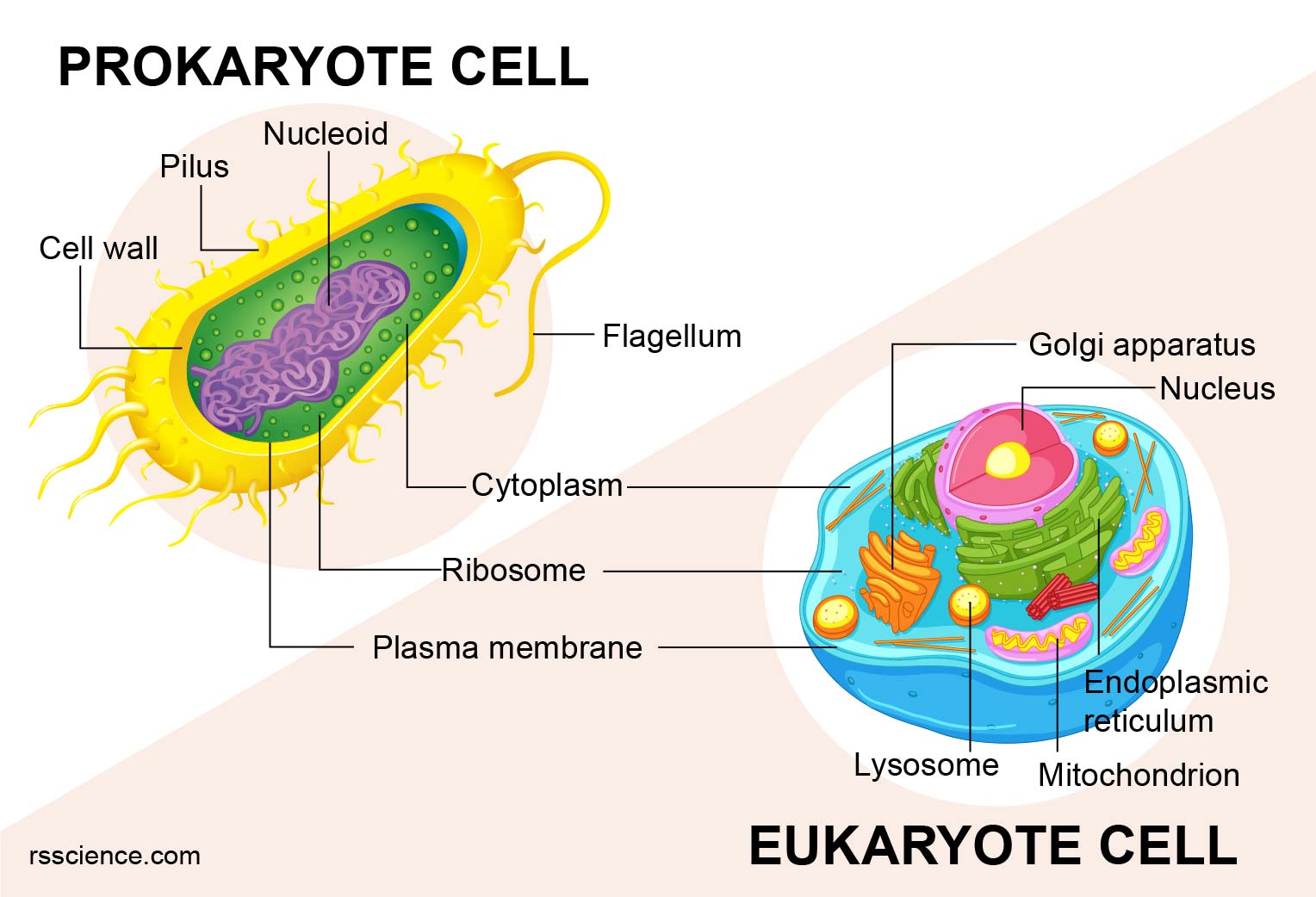
Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes What Are The Similarities Differences And Examples Rs Science

Pdf Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Gene Structure Semantic Scholar

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary
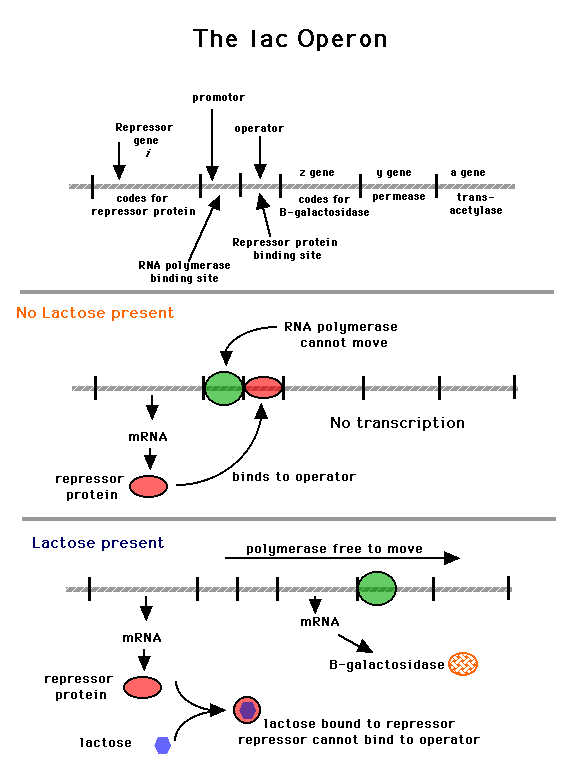
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic Genes Eukaryotic Genes And Operon Socratic
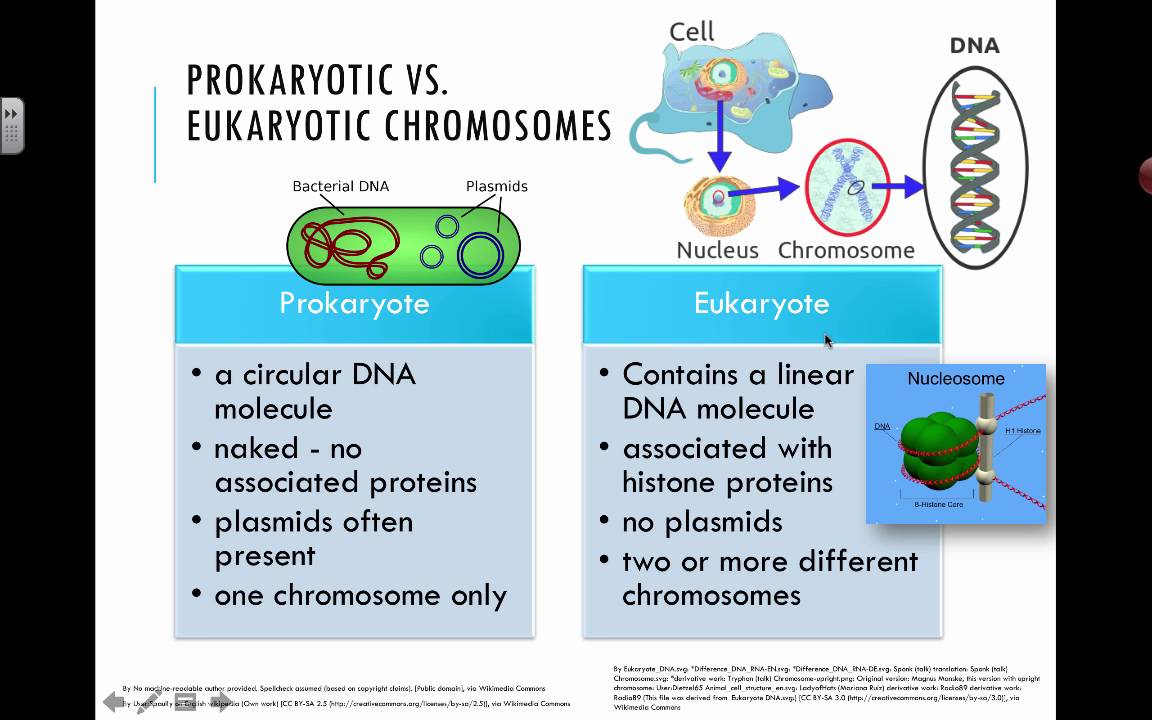
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Chromosomes 2016 Ib Biology Youtube
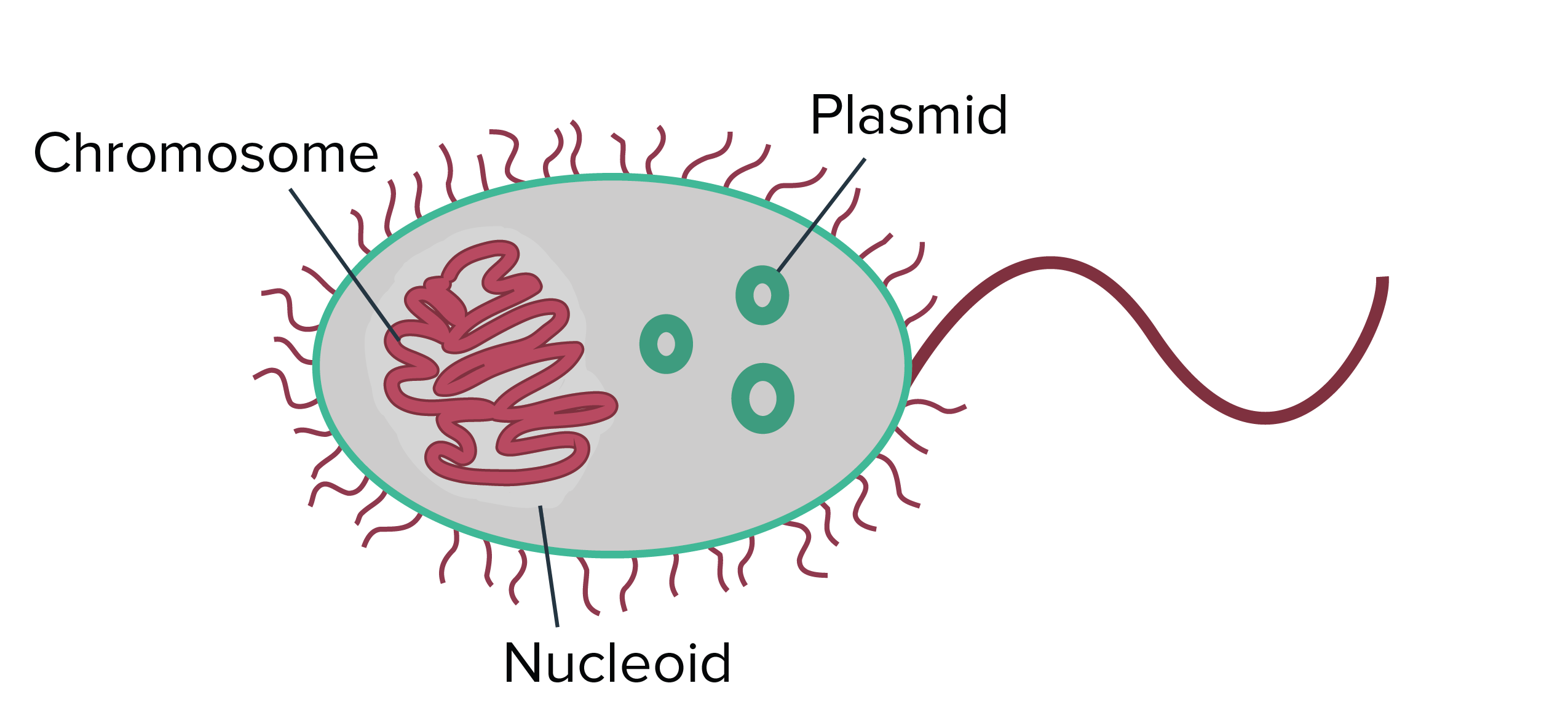
Prokaryote Structure Article Khan Academy

Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell Difference And Comparison Diffen Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotes

Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Genome Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
3 2 Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
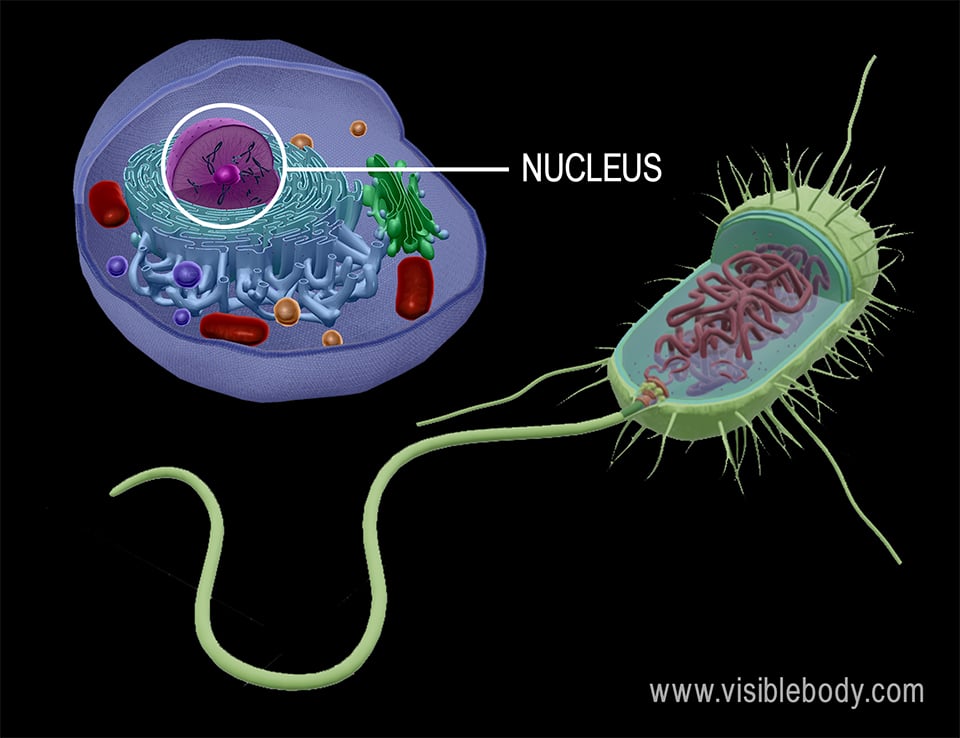
Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Chromosomes
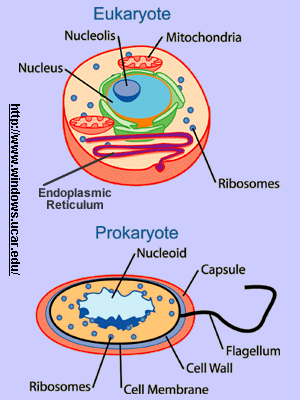
Eukaryotes Vs Prokaryotes Similarities Differences And Organelles
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Gene Structure Pediaa Com
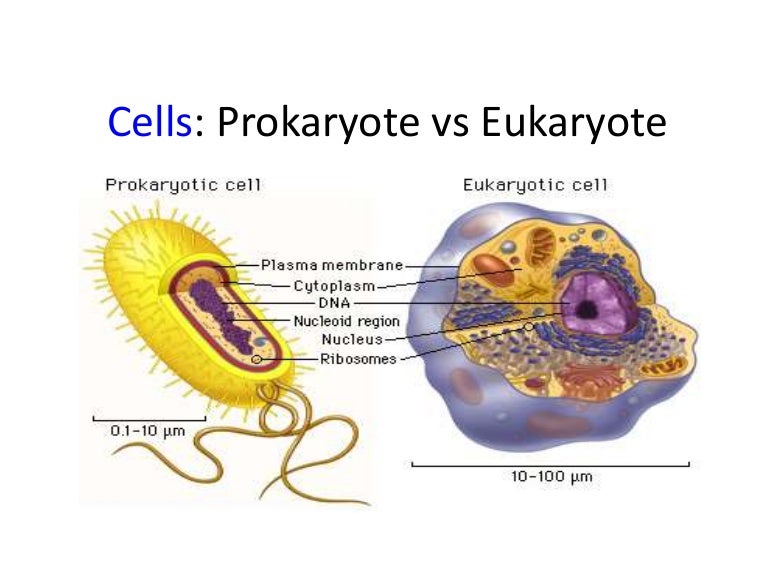
Comments
Post a Comment